-
Merit Badges
- Legend to identify Merit Badges
- 1910 British Merit Badges
- Square 1911 - 33
- Wide Crimped 1934 & 35
-
Narrow Tan Crimped 1936 - 42
- Tan Heavyweight Cloth with Silk Embroidery and Printed Back 1936 - 37
- Tan Heavyweight Cloth with Silk Embroidery and Plain Back 1937 - 38
- Tan Lightweight Cloth with Silk Embroidery and Plain Back 1938 - 39
- Tan Lightweight Cloth with Cotton Continuous Loop Embroidery and Plain Back 1939 - 42
- Tan Lightweight Cloth with Cotton Lockstitch Embroidery and Plain Back 1939 - 42
- Blue Background 1942 - 46
- Wartime 1942 - 46
- Khaki Narrow Crimped 1946 - 59
- Green Twill Gauze Back 1960 - 68
- Fully Embroidered Merrowed Edge 1960 - 72
- Unprinted Plastic Back 1972 - 01
- Printed Plastic Back 2002 - Current
-
Merit Badge Paper
- Merit Badge Applications
- Merit Badge Cards
-
Merit Badge Pamphlets
- Type 1 White Cover - Rectangle Drawing On Cover
- Type 2 White Cover 5-375" x 8" Title at Top
- Type 3A Tan Cover - 200 Fifth Avenue
- Type 3B Tan Cover - 2 line address New York City
- Type 3C Tan Cover - 2 line address New York N.Y.
- Type 3D Tan Cover - 1 line address New York N.Y.
- Type 4 Standing Scout Cover
- Type 5A War Cover
- Type 5B Red and White
- Type 6 Photo-Red Cover
- Type 7 Full Photo Cover or Bulls-eye Cover
- Type 8 Full Photo - Green Stripe Cover
- Type 9 Full Photo - Red Stripe Cover
- Type 10A Blue Stripe - Logo above bottom blue stripe - FDL centered
- Type 10B - Blue Stripe in bottom of photo area. FDL to left of text
- Special Covers
- Boy Craft Helps
- Merit Badge Counselor's Guides
-
Youth Position
- Junior Assistant Scoutmaster
- Senior Patrol Leader
- Assistant Senior Patrol Leader
- Patrol Leader
- Assistant Patrol Leader
- Troop Guide
- Scribe
- Quartermaster
- Instructor
- Chaplain Aide
- Den Chief
- Librarian
- Musician
- Webmaster
- Bugler
- Troop Historian
- Troop Representative
- Unit Representative
- Leadership Corps
- Honor Guard
- Leave No Trace Trainer
- Outdoor Ethics Guide
- Patrol Medallions

Fig. 1: Wirele-AH-Front
- Cloth: Heavyweight tan
- Embroidery: Silk continuous
- Border: Clockwise, round & dense
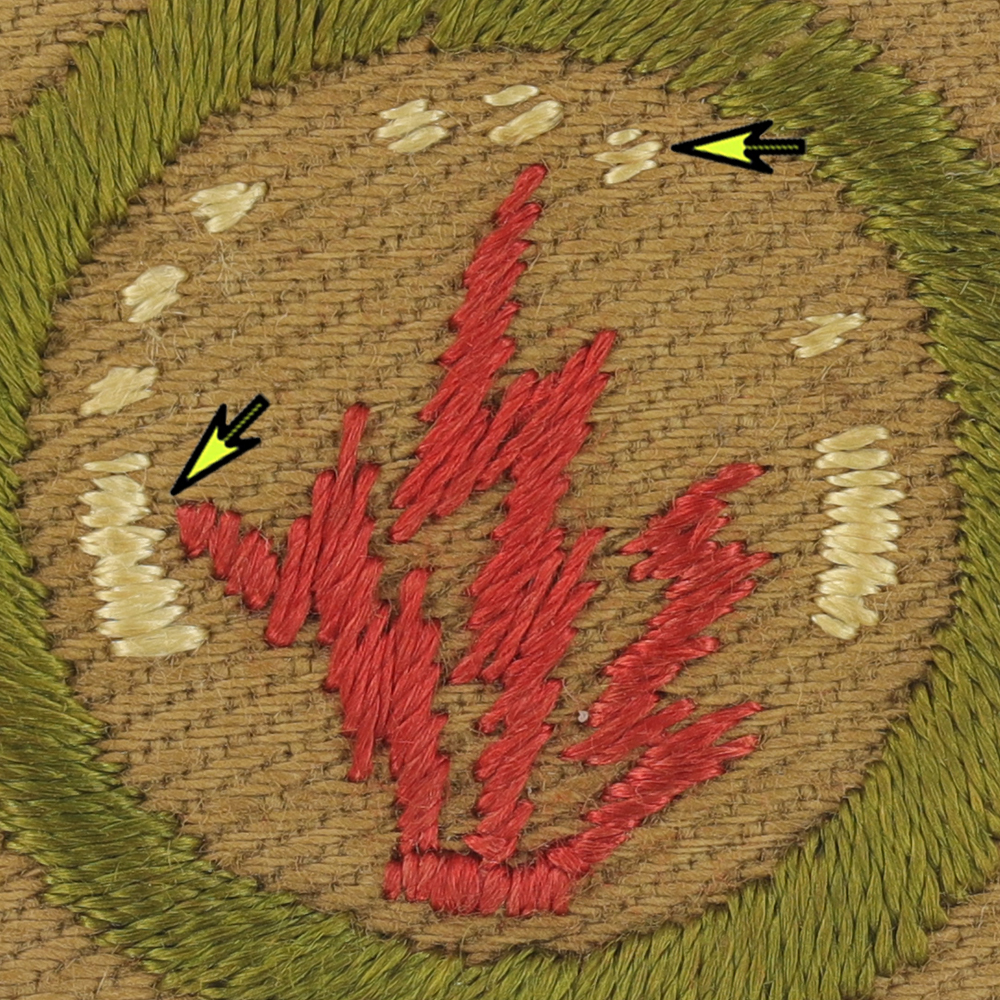
Fig. 2: Wirele-AH-Magnified
- Design: Left red end spike lower than highest spike on left lighting bolt, "S" dots horizontally stitched

Fig. 3: Wirele-AH-Reverse
- Back: Black imprint
Item Name: Wireless 1919 - 1921
Item ID: Wirele-AH
Collector Rating: 1
Pamphlets Used to Earn this Badge
Requirements December 1918 until May 1919
- Be able to receive and send correctly not less than ten words a minute.
- Know the correct form for sending a message.
- Be able to tell in own words the principal laws regarding radio communication.
- Know at least ten of the radiogram abbreviations. (Q signals.)
- (a) Be able to name two types of detectors and explain how they work.
(b) Name five minerals used in detectors in the order of their sensitiveness.
- Draw a diagram of a simple transmitting set, showing how the following instruments are connected: dynamo or storage battery (source of power), transformer, condenser, spark, gap, helix, key. Explain the function of each.
- Draw a simple diagram showing how to connect the following instruments; tuning coil or loose coupler, condensers, fixed or variable detector, phones and ground. Tell the use of the above apparatus.
- Draw a diagram of three different types of aerials and tell their advantages or faults.
- (a) Know how to properly ground a radio set and know what precautions to take during a thunder shower.
(b) Demonstrate how to rescue a person in contact with a live wire, and have a knowledge of the method of resuscitation of a person insensible from shock.
- Write a brief essay on development of wireless telegraphy.
Requirements May 1919 until August 1922
- Be able to receive and send correctly not less than ten words a minute.
- Know the correct form for sending a message.
- Be able to tell in own words the principal laws regarding radio communication.
- Know at least ten of the radiogram abbreviations. (Q signals.)
- (a) Be able to name two types of detectors and explain how they work.
(b) Name five minerals used in detectors in the order of their sensitiveness.
- Draw a diagram of a simple transmitting set, showing how the following instruments are connected: dynamo or storage battery (source of power), transformer, condenser, spark, gap, helix, key. Explain the function of each.
- Draw a simple diagram showing how to connect the following instruments; tuning coil or loose coupler, detector, fixed or variable condensers, phones and ground. Tell the use of the above apparatus.
- Draw a diagram of three different types of aerials and tell their advantages or faults.
- (a) Know how to properly ground a radio set and know what precautions to take during a thunder shower.
(b) Demonstrate how to rescue a person in contact with a live wire, and have a knowledge of the method of resuscitation of a person insensible from shock.
- Write a brief essay on development of wireless telegraphy.

